Design
/
Taze Creative
In recent years, there has been a notable increase in the use of technology within the healthcare sector. From accelerating drug discovery to analyzing medical records for improved diagnosis, numerous instances highlight how technology has been a driving force behind the industry's growth. This leads us to an equally important concept: Healthcare UX.
Picture this: a hospital with clear signage that's easy to follow or a medication label with straightforward instructions. These are prime examples of effective UX design in healthcare, making processes smoother and more accessible for patients and professionals alike.
The healthcare sector extends far beyond medical diagnosis. It also involves maintaining or improving health through the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and recovery from illness, injury, and other physical or mental conditions. This broad scope includes services provided by medical professionals, hospitals, clinics, and various healthcare institutions.
Healthcare UX, or user experience in healthcare, focuses on creating user-friendly experiences for everyone involved in the medical field. This applies to both digital platforms and physical interactions within healthcare settings.
Here are its core goals:
Improved Patient Satisfaction and Engagement
Increased Efficiency for Providers
Enhanced Accessibility
Improving user experience is a central goal in every industry, and healthcare is no exception. As the healthcare sector transitions from vast amounts of data to digital platforms, creating user-friendly interfaces has become crucial for healthcare UX design. This applies to both digital products and physical interactions.
Picture an easy-to-use appointment scheduling app or clear instructions on a medication label—these are examples of effective healthcare UX design.
By focusing on user needs, healthcare UX design aims to:
Improve patient satisfaction and engagement: A clear interface and easy access to health records can greatly enhance patient experience.
Enhance healthcare providers' efficiency: Streamlining workflows and reducing errors helps healthcare professionals perform their jobs more effectively.
Increase accessibility: Designs should cater to individuals with disabilities or limited technical skills, ensuring that healthcare data is accessible to all.
If you're building a healthcare product, it’s essential to explore the latest healthcare UX design trends to stay ahead.
Ultimately, good healthcare UX design is more than just about convenience; it promotes better health outcomes, saves time, and reduces costs.
Despite the rapid growth of the digital healthcare sector, a significant UX issue lies in the complex interface of electronic medical record (EMR) systems, which often require extensive training to navigate efficiently.
Additionally, transferring data between hospitals presents challenges. Text-based files make it difficult for medical professionals or healthcare apps to quickly locate medications, diagnoses, or gain a clear understanding of a patient's medical history. Healthcare workers also face the burden of remembering multiple lengthy passwords for different accounts when sharing reports. This adds stress to doctors and nurses who already work long hours and irregular shifts.
The audience for healthcare applications includes not only professionals like doctors and nurses but also patients from diverse backgrounds. The challenge is ensuring that healthcare information is accessible and meets the needs of both patients and medical professionals.
5 key challenges in healthcare UX design

Detailed workflows
Managing appointments and prescriptions for thousands of patients is a significant challenge. Medical UX designers must create workflows that are intuitive and efficient for both patients and healthcare providers, streamlining data management processes.Aligning user demands with compliance regulations
Data privacy is crucial in healthcare. While designing user-friendly features, medical UX designers must ensure compliance with stringent regulations to safeguard sensitive patient information.Inclusive access for everyone
Healthcare applications need to be accessible to a wide range of users, including individuals with disabilities or limited technical skills. UX designers must create easy-to-understand interfaces that offer seamless, inclusive interaction.Data visualization
Medical data can be overwhelming, even for healthcare professionals. The challenge is to present complex data in a clear, concise, and easily digestible format for efficient decision-making.Empathy and sensitivity
Healthcare services are often used during stressful or vulnerable moments. UX design must be sensitive to these emotions by creating interfaces that are calming, supportive, and easy to navigate, reducing user anxiety.
To effectively address challenges in healthcare UX design, it’s essential to conduct user research for both segments—professionals and patients. This research will reveal common terms, pain points, and insights into the healthcare industry, enabling the development of applications that improve healthcare UX.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to tackle the five challenges discussed:
1. Detailed workflows
User research & process mapping
Conduct in-depth interviews and shadowing sessions with both patients and healthcare providers to identify pain points in current workflows. Mapping out each step in the process will reveal areas of confusion and inefficiency.
Prioritization & simplification
After mapping workflows, prioritize the most frequent and critical user journeys. The UX designer should focus on simplifying these key journeys by organizing information logically. Progressive disclosure can be employed, ensuring users only see essential information at the start, with more details revealed as needed.
2. Aligning user demands with compliance regulations
Early collaboration
Establish a clear communication flow between UX designers, legal teams, and compliance officers from the outset. This ensures that key regulations are understood and incorporated into the design process, helping the app meet all necessary legal and security standards.
Secure and user-friendly solutions
Focus on design patterns that prioritize both security and ease of use. For instance, implementing two-factor authentication can strengthen security without making the login process unnecessarily complex for users.
3. Inclusive access for everyone
User research with diverse groups
To create a truly user-friendly healthcare app, it's essential to conduct research with a wide range of users, including individuals with disabilities and those who are less tech-savvy. By understanding their unique needs and challenges, UX designers can enhance user engagement and ensure the app is accessible to all.
WCAG compliance
Follow the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to ensure the app meets accessibility standards. This includes features like screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and ensuring content is perceivable, operable, and understandable for users with disabilities.
4. Data visualization
User personas & content strategy
Create detailed user personas that reflect different audience segments, such as patients, doctors, and administrators. Tailor the presentation of data based on users' medical knowledge and needs, making complex information easier to understand for each group.
Visual hierarchy & interactive elements
Implement a clear visual hierarchy and incorporate interactive elements like charts, graphs, and filters. These features allow users to explore and engage with the data as needed, ensuring the information is both accessible and meaningful.
5. Empathy and sensitivity
User empathy & emotional Design
Understand and empathize with the emotional states users may experience, such as anxiety or frustration while navigating the healthcare system. Designing with empathy ensures that the user’s emotional needs are considered throughout the process.
Calming aesthetics & supportive language
Incorporate calming color schemes, simple language, and positive messaging to create a reassuring user experience. Provide clear instructions and progress indicators to help reduce anxiety and give users a sense of control and confidence.
By following these steps and keeping user needs at the forefront of the design process, healthcare UX professionals can craft user-friendly experiences that manage the complexities of the healthcare system. These solutions will not only comply with regulations but also remain sensitive to users' emotional states, ensuring a supportive and accessible environment for all.
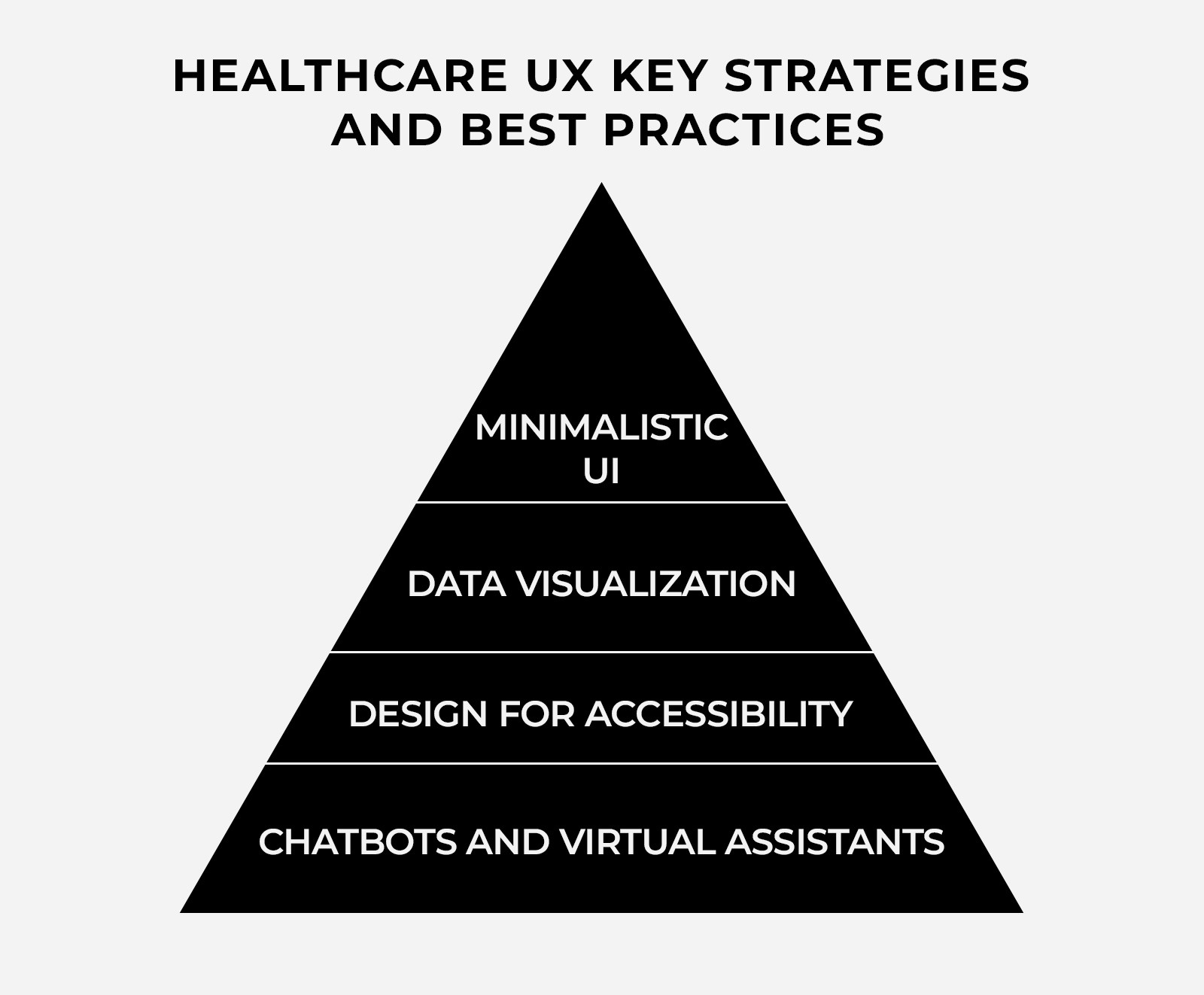
1. Minimalistic UI
A minimalistic UI is crucial in healthcare UX, where users must access large amounts of information. The key is to present data clearly and concisely, allowing diverse users to navigate the app easily. This approach helps users quickly find what they need, focusing attention on important information and reducing cognitive load.
While the complexity of healthcare data shouldn't be eliminated, it should be well-managed, especially when dealing with nuanced information like statistical analysis. Best practices, such as progressive disclosure and a minimalistic color theme, can help. Using calming colors like blue can reduce stress for both patients and medical professionals, creating a more reassuring environment.
2. Design for accessibility
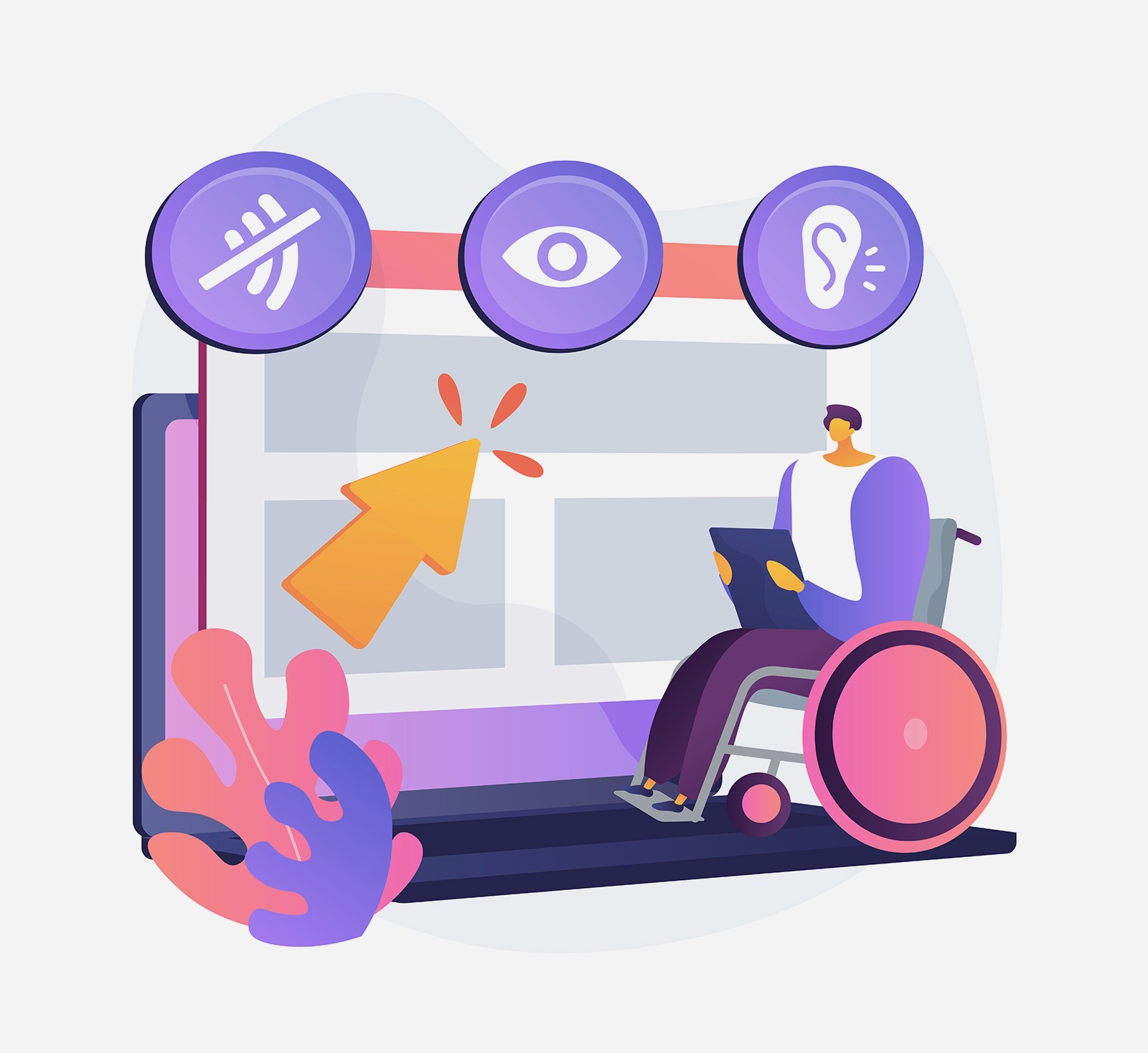

When designing healthcare UX, it's important to consider that while doctors and nurses are educated professionals, patients come from various backgrounds, including the elderly and individuals with disabilities. According to WHO, 15% of the global population has some form of disability, and this percentage is likely even higher within the healthcare sector.
To ensure inclusivity, healthcare UX should incorporate the following:
Larger fonts for readability
High color contrast for visual clarity
Simple, straightforward language
Easy-to-navigate interfaces
Accessibility features like text-to-speech, captions, and video options
These elements not only make information accessible to the elderly and people with disabilities but also enhance the user experience for everyone. Just as subtitles help in noisy environments, accessibility features can benefit all users, ensuring a smoother and more inclusive interaction.
3. Data visualization

Data visualization is crucial in healthcare UX, as it helps present complex healthcare information in a manageable and efficient way. Lengthy, detailed reports can be transformed into colorful charts and graphs, allowing users to quickly grasp key points at a glance.
For healthcare professionals, visualized data makes it easier to spot patterns, establish correlations, and extract insights. For patients, it enables tracking of their medical history and understanding health reports without needing to navigate through medical jargon and complicated information.
4. Chatbots and virtual assistants

Even with the most user-friendly interface, users may still struggle to find specific information. This is particularly challenging in healthcare, where vast amounts of data need to be accessed by medical professionals, often at odd hours, to treat patients.
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can help address this issue by providing instant, 24/7 support. These tools not only answer common queries but can also book doctor appointments and guide users to relevant information, reducing the burden on human staff.
By integrating chatbots, healthcare organizations can improve communication between hospitals, medical professionals, and patients, making the overall experience more efficient and user-friendly.
5. AI-powered technology

Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries across the board, and healthcare is no exception. While AI-powered chatbots are a prime example, AI’s applications in healthcare extend much further. AI can automate routine tasks, such as scheduling appointments, sending reminders, and handling data entry. It can also analyze large datasets, including electronic patient records and test results, to identify patterns and generate insights with greater accuracy than humans can achieve.
Additionally, AI can personalize care by using patient data and behavior to offer tailored recommendations, improving both user retention and satisfaction in healthcare services.
For years, healthcare applications developed by software developers and UX designers have often fallen short of meeting the needs of medical professionals and patients. The healthcare industry requires UX designers with specialized expertise in creating user-friendly healthcare apps.
Healthcare UX designers must understand their audience and be well-versed in industry-specific terminology. If you're looking to improve your healthcare app or website, our team of healthcare UX specialists at Alien Design is the perfect fit for building effective healthcare products. Our user-centric approach ensures that the design process is aligned with the specific requirements of our clients.