Online Ads
/
Taze Creative
Google Ads, formerly known as Google AdWords, is Google’s digital advertising platform. It offers various ad formats, including text, images, and videos, that appear on Google search results and across the Google Ads Network. This network helps businesses reach people searching for relevant products or services. Google Ads can increase website traffic, generate more business inquiries, and drive purchases.
When creating an ad on Google, you must set a maximum bid, which is the most you are willing to pay. Google Ads operates on several payment models:
Cost-per-click (CPC): Pay when someone clicks on your ad.
Cost-per-mille (CPM): Pay per 1,000 ad impressions.
Cost-per-engagement (CPE): Pay when a user takes a specific action, such as signing up for a newsletter or watching a video.
The auction process determines where your ad will appear. Google considers the following factors when determining ad placement:
Bidding Process: How much you are willing to pay for each click or action.
Quality Score (QS): How relevant your ad and landing page are to the targeted keywords.
Assets: Additional elements, such as a phone number or business location, that can enhance the ad’s impact.
Ads with higher scores (a combination of bidding and quality) are more likely to appear at the top of search engine results pages (SERPs).
Steps to advertise on google
Create a google ads account
Start by visiting the Google Ads website and create an account.
Enter your business name, website URL, and billing information.
Optionally, link other Google-owned accounts like YouTube or your Google Business Profile for better ad personalization.
Arrange your account
Click on “New Campaign” on the dashboard and set a goal for your campaign.
Organize campaigns and ad groups, with each campaign focusing on broader categories (e.g., "burgers") and each ad group targeting specific aspects (e.g., "vegetarian burgers").
Set a Budget
Set a daily budget and define your bids, which is how much you're willing to pay for a click on your ad.
If you’re new to Google Ads, allow Google to auto-optimize your bids for maximum efficiency.
Identify your target audience
Define your audience by specifying demographics like gender, age, and location (e.g., targeting a specific city).
Refine your target segments based on customer interests and life events to make sure your ads are seen by the right people.
Select an ads network
Choose between the Google Search Network (GSN) or the Google Display Network (GDN):
GSN: Ads appear on search engine results, great for direct searchers.
GDN: Ads appear across Google’s Display Network, better for retargeting previous visitors.
Choose your keywords
Select 15-20 keywords that your target audience might use when searching for your product.
Google’s Keyword Planner can suggest relevant keywords. For beginners, it's often better to target lower-competition keywords for better results.
Configure your keyword matches
Refine how your ads appear by choosing from:
Broad Match: Ads appear for a wide variety of related searches (e.g., "chopped steak" for "burger").
Exact Match: Ads appear only for close keyword matches (e.g., "hamburger" for "burger").
Phrase Match: Ads show for variations of your keywords (e.g., "cheeseburger" for "burger").
Negative Keywords: Exclude certain terms to avoid irrelevant traffic (e.g., excluding “cheap” if selling high-end products).
Link your landing pages
Ensure the ad links to a relevant landing page that matches the offer or product in the ad.
For example, if you are promoting vintage 1970s pins, the ad should link directly to that product page, not a general homepage.
Select a preferred device
Choose whether you want your ads to display on mobile, desktop, or both, depending on your target audience.
For example, ads for a fast-food restaurant might perform better on mobile devices.
Create your google ads
Provide the necessary ad components:
A URL for the landing page.
Up to 15 headlines and 4 descriptions.
Images (if applicable).
4+ site links (additional specific links under the ad).
Call to action (CTA), encouraging users to act (e.g., "Shop Now").
Google’s AI will test and display the best-performing combinations.
Make Google Ads payment
Google Ads will prompt you to set up payment before launching the campaign. Refer to Google’s Account & Billing guide for more details on payment options.
Link Google Ad to Google Analytics
Connect your Google Ads account to Google Analytics for detailed performance tracking.
This integration helps you analyze how users interact with your ads and refine your strategy.
Launch your Google Ad campaign
Activate the campaign and start sharing your ads with your target audience.
Continuously monitor performance, review which keywords perform best, and adjust ads accordingly for optimal results.
The cost of Google Ads campaigns can vary significantly depending on several factors. The main factors that influence the cost include:
Ad Type: Different ad formats, such as search ads, display ads, and video ads, come with varying costs.
Campaign Goal: Whether the goal is brand awareness, lead generation, or sales conversion will affect pricing.
Keywords: High-demand keywords are more expensive to bid on, especially those with significant competition.
Keyword Search Volume: Keywords with higher search volumes are more expensive as there is more competition to appear in those searches.
Headline Copy: The quality and relevance of the ad’s headline can impact bidding costs.
Ad Schedule: Ads that are shown during peak hours (e.g., weekends, evenings) or peak seasons (e.g., holidays) may cost more due to higher competition.
Expected Reach: Campaigns targeting larger audiences tend to cost more.
Ad Creative: High-quality images, videos, and dynamic formats may affect the performance and cost of the ads.
Manual vs. Automatic Bidding: Manual bidding allows you to control costs, while automatic bidding might increase spending based on optimized results.
For instance, search and display ads are typically more competitive and require higher bids, especially during peak hours when more users are actively engaging online.
According to Statista, the average cost per click (CPC) for Google Ads in the U.S. is around $1.99, but this can fluctuate significantly based on the factors above.
Types of Google Ads
Google provides a variety of ad types, each designed to meet different campaign goals and target audiences. Below are the primary types of Google Ads:
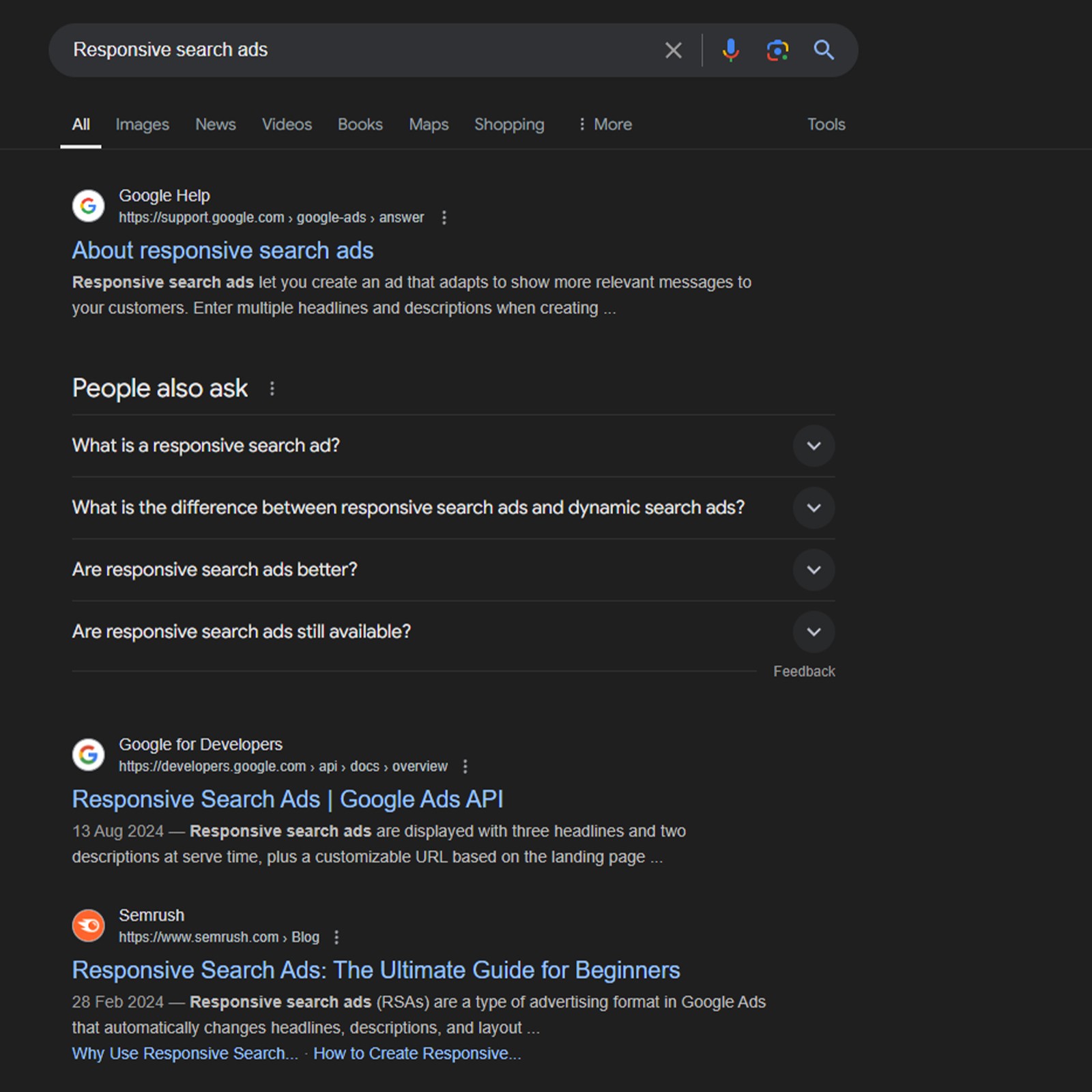
1. Responsive search ads
Responsive search ads are text-based ads that appear in search results when users search for related keywords. These ads typically show the website name, a title tag, and a meta description. You can create multiple text variations for Google to choose from and match with user queries.
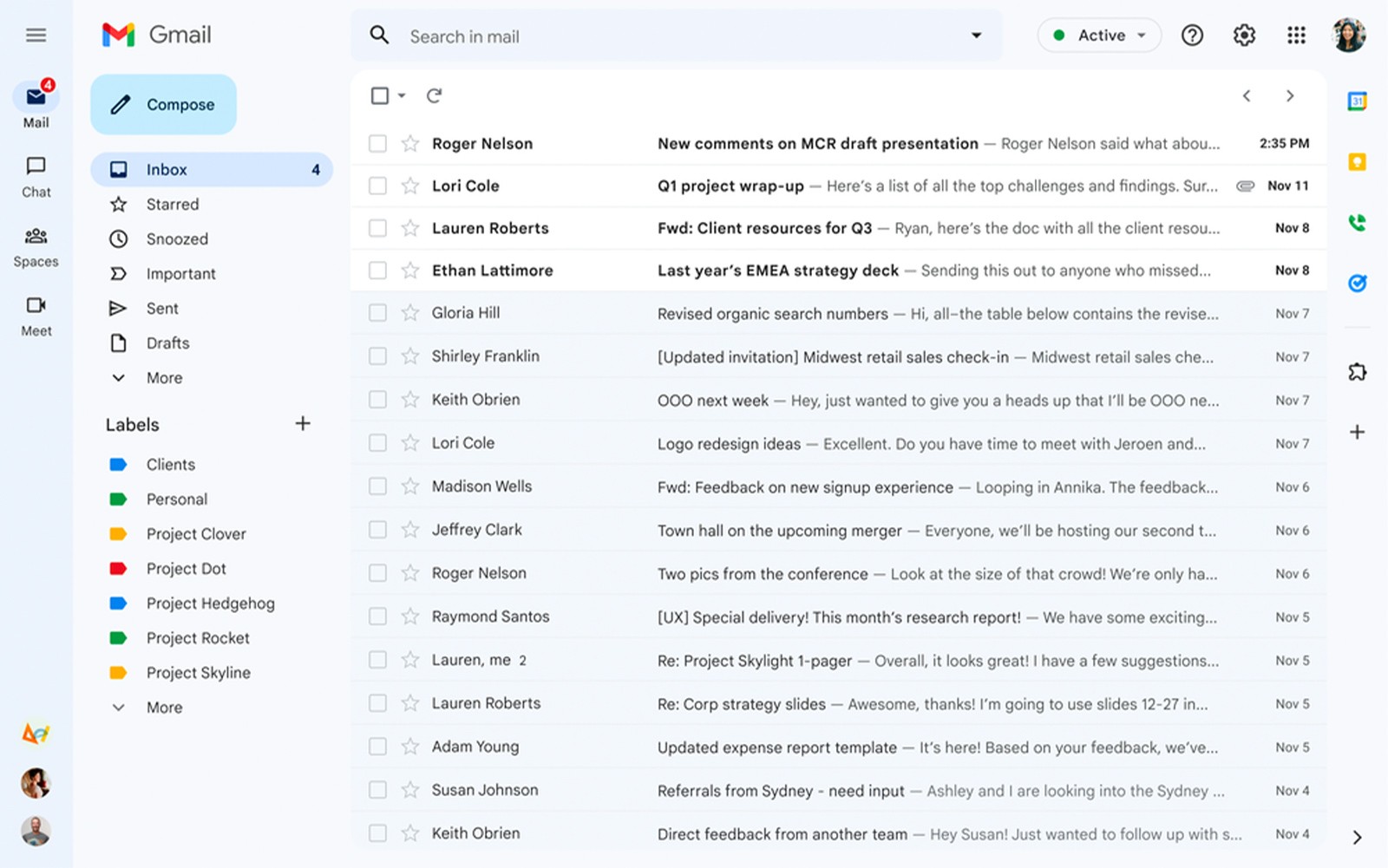
2. Discovery ads
Discovery ads combine the features of display ads and shopping ads. They are highly visual and appear on platforms like YouTube’s homepage, Gmail's Promotions and Social tabs, Discover feeds, and Google search results for purchase-related queries. These ads are designed to target users who are already in the consideration phase of their buying journey. Google uses data such as:
User web and app activity
Device app information
Location history
Discovery ads can reach up to 3 billion people across Google's platforms.
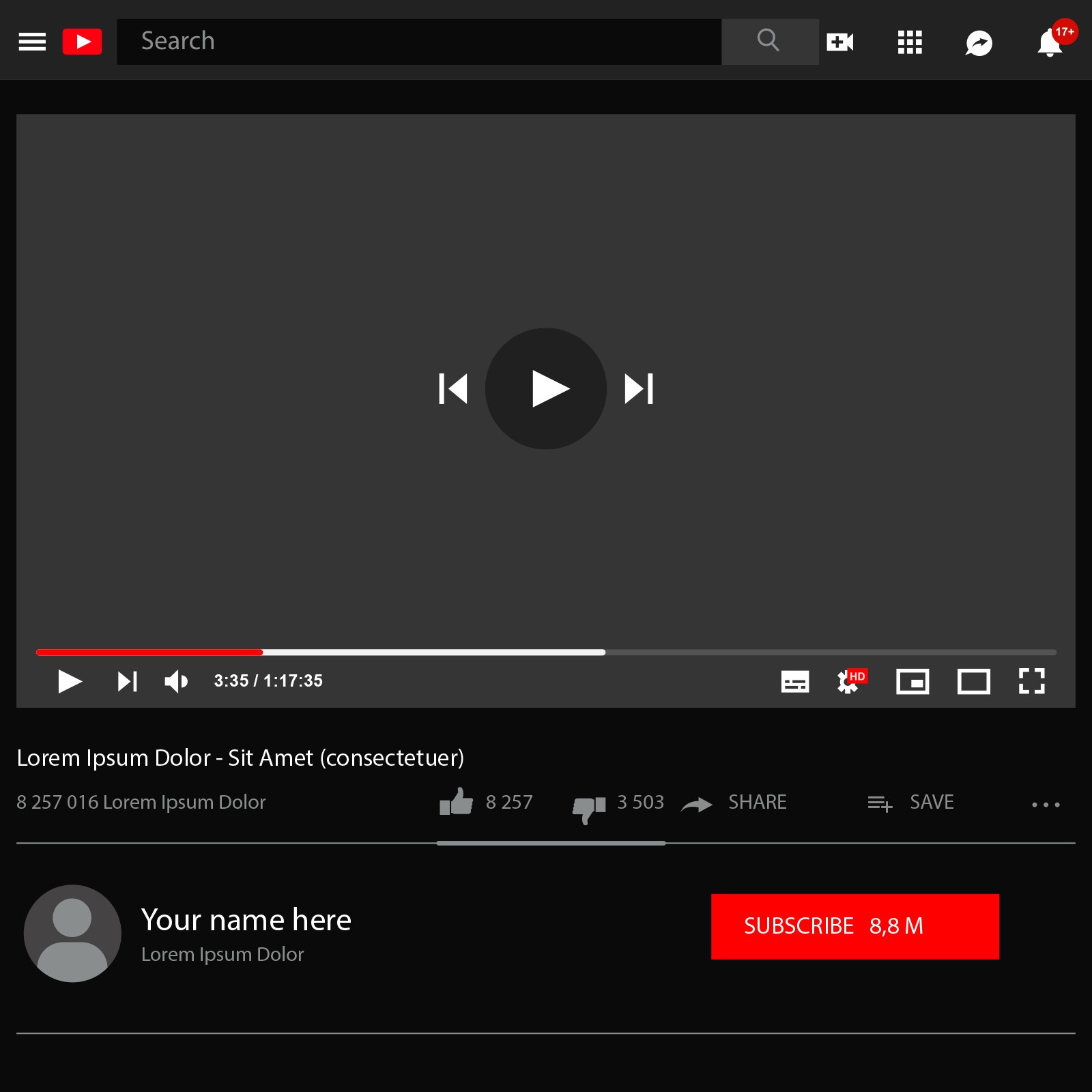
3. Video ads
Video ads are primarily shown on YouTube and Google's video ad partners. These ads play before, during, or after YouTube videos, on the home feed, search feed, "Watch Later" lists, and playlist pages. Video ads are ideal for product launches or announcing new offers. They’re tailored based on users’ watch history and interests.
Popular formats include:
Bumper Ads: Six-second, non-skippable ads that play before videos.
In-Stream Ads: Skippable after five seconds or non-skippable ads that play before, during, or after videos.
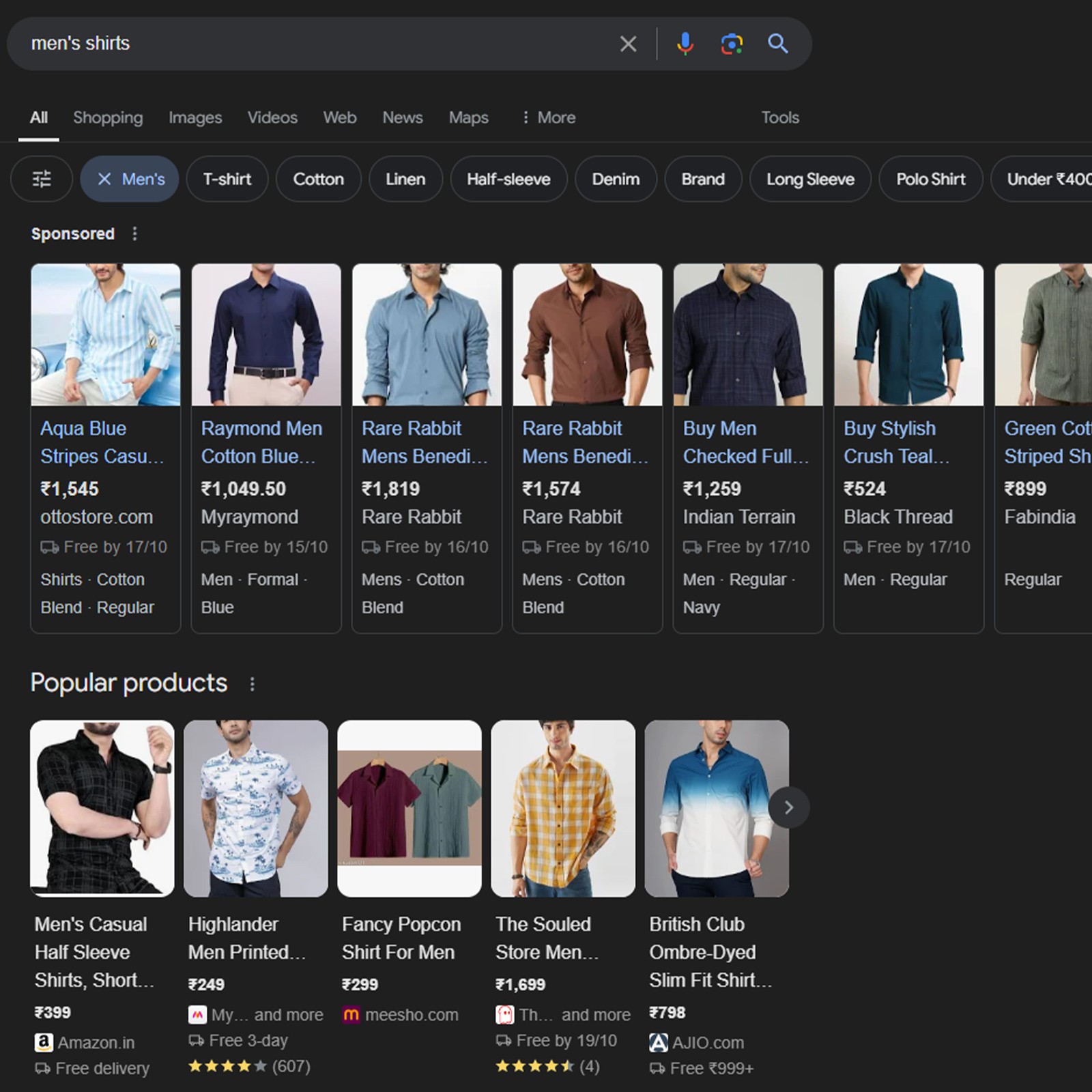
4. Shopping ads
Shopping ads are designed for e-commerce businesses and appear on Google’s search and display networks, YouTube, and Gmail. These ads feature product listings with images, prices, and links, making it easy for users to browse and purchase directly. For example, when someone searches for “freelancer shirt,” Google will display a product carousel or a listing of available options. These ads are ideal for retailers with a product inventory to promote.
5. App ads
App ads drive more app installs and engagement, appearing on Google Search, Play Store, App Store, Google Discover, and YouTube feeds. These ads are suitable for both Android and iOS apps, and Google automatically optimizes placements to increase engagement. App campaigns can also include pre-registration campaigns to encourage users to sign up for an app before its official launch.
Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your existing campaigns, following these best practices for Google Ads will help you achieve better results and boost revenue.
1.Automate campaigns with Google AI.
Leverage Google’s artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize your ads. By creating multiple versions of your ads, Google’s AI can rotate these variations and learn which ones perform best. This helps improve conversions and sales as Google automatically shows the top-performing ads to your target audience.
2. Improve your quality score (QS).
Your ad’s position on the search engine results page (SERP) depends heavily on its Quality Score (QS). A high QS can lower your cost per click (CPC) and improve your ad rank. To boost your Quality Score:
Ensure your ad is highly relevant to the targeted keywords.
Match the landing page content with the keywords.
Maximize your expected click-through rate (CTR).
Check your Quality Score regularly in the Google Ads dashboard and refine your campaigns accordingly.
3. Write catchy headlines
Craft concise, attention-grabbing headlines. Google Ads allows up to 15 headlines of 30 characters each, so maximize the space to create variations that build on each other. For example:
"Sunglasses for Sale"
"Find Your Perfect Frames"
"Shop Our Collection"
These headlines tell users what your business offers and encourage them to click through.
4. Include succinct descriptions
Use the description fields to communicate what makes your business stand out. You have three description lines of 90 characters each, so be clear and persuasive. For instance:
“Over 70 styles to choose from, plus free shipping anywhere in the U.S.”
This description highlights your business’s unique selling points and encourages users to take action.
5. Use appropriate keywords
Selecting the right keywords is crucial for ad success. Long-tail keywords are often more effective because they target specific user intent. For example, instead of using “hamburger,” opt for a more location-specific keyword like “hamburger in Kissimmee” to reach your ideal audience.
Monitor keyword search volumes and avoid highly competitive ones when starting. Choose relevant keywords that are moderately competitive to maintain cost-effectiveness.
6. Use Google assets
Google Ads allows you to enhance your ads with additional features, known as assets. These include:
Site links: Direct users to different pages of your website.
Images: Visually engage your audience.
Business phone number: Encourage direct contact.
Location: Highlight proximity to potential customers.
Price listing: Showcase competitive pricing.
App download button: Promote app installs.
These assets can make your ad more engaging and help customers reach you faster.
7. Optimize your landing page
Your landing page plays a key role in turning ad clicks into conversions. Ensure the content matches the keywords and intent behind your ad, and make the call to action (CTA) clear. Additionally, ensure your landing page is mobile-responsive and user-friendly to capture leads or sales effectively.
8. Double-check your ad details
Before launching your campaign, thoroughly review your ad details. This includes:
Checking for spelling and grammar errors.
Verifying that links direct users to the correct pages.
Ensuring that all keywords are included and relevant.
Typos or broken links can harm your ad’s performance, so it’s essential to get everything right before going live.
9. Test different ads
Even if your ad performs well, continuous improvement is essential. A/B testing allows you to try different variations of your ad, such as:
New keywords
Alternative headlines or descriptions
Different images or videos
By testing multiple versions, you can identify which elements drive the best results and refine your campaigns accordingly.
Advertising on Google using Google Ads is an effective way to promote your business and increase the chances of reaching your target customers. By setting up your campaigns correctly and following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can optimize your ads to drive more traffic, conversions, and sales. With the flexibility of Google Ads, businesses of all sizes can benefit from a tailored ad strategy to meet their specific marketing goals.



